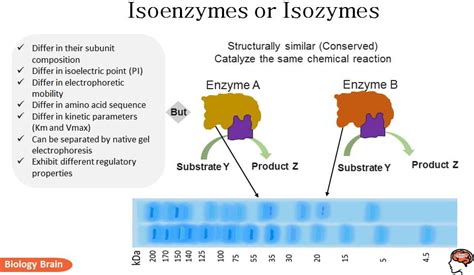
isoform vs isozyme|What are the differences between isozymes, allozymes and : Manila In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. different KM values), or are regulated differently. They permit the fine-tuning of metabolism to meet the particular needs of a given tissue or developmental stage. 2048. 0. 0. Join the numbers and get to the 2048 tile! Keep going Try again. How to play: Use your arrow keys to move the tiles. When two tiles with the same number touch, they merge into one! Created by Allyson Schrader, to create a .
isoform vs isozyme,Isozymes are derived from different genes but perform similar functions. Allozymes are derived from the same gene but different loci, functionally conserved. Isoforms are a result of post transcriptional modification of the same gene, I am not .
isoform vs isozyme Abstract. Isoforms are highly related gene products that perform essentially the same biological function. Isozymes are isoforms of an enzyme. Isoforms can differ .In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. different KM values), or are regulated differently. They permit the fine-tuning of metabolism to meet the particular needs of a given tissue or developmental stage.isoform vs isozyme What are the differences between isozymes, allozymes and In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. different KM values), or are regulated differently. They permit the fine-tuning of metabolism to meet the particular needs of a given tissue or developmental stage.A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For .

Actins are proteins that are essential for a number of fundamental cellular processes such as cell division and muscle contraction. In mammals, there are six actin .

Actins are proteins that are essential for a number of fundamental cellular processes such as cell division and muscle contraction. In mammals, there are six actin . Isozymes allow metabolism to be fine-tuned to fit the specific demands of a certain tissue or developmental stage (for example, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)). . The isozymes of this enzyme are divided into two forms, the H isozyme and the M isozyme. The H isozyme is expressed more in the heart, whereas the M .
The enzymes that occur in a number of different forms and differ from each other chemically, immunologically and electrophoretically are called “Isoenzymes” or .
isoform vs isozyme|What are the differences between isozymes, allozymes and
PH0 · What are the differences between isozymes, allozymes and isoforms?
PH1 · What are the differences between isozymes, allozymes and
PH2 · Structural Biochemistry/Enzyme Regulation/Isozymes
PH3 · Protein isoform
PH4 · Protein Isoforms and Isozymes
PH5 · Isozymes: Definition, Occurrence and Characteristics
PH6 · Isozymes: Definition, Function, and Examples I ResearchTweet
PH7 · Isozymes
PH8 · Isozyme
PH9 · Isoforms: Fundamental differences
PH10 · ENZYME ISOFORMS MAY INCREASE PHENOTYPIC